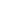
Heavy-duty extension springs, also called tension springs, store up energy and resist pulling forces. Also known as tension, when these pulling forces cease to act on the spring it then returns to its original shape. Sometimes they are confused with compression springs, which compress under loads instead of resisting tension. The tightly wound coils of these springs stretch under loads and are used to control motion, or to counteract forces applied to a piece of equipment. These extension springs are used in applications where tension must be maintained, or when two components need to be brought back together.
The Role of Heavy-Duty Extension Springs in Mechanical Systems
The main purpose for heavy-duty extension springs involves absorbing and storing energy. They extend when loads pull the coils apart then relax once the force is removed, which allows the item controlled by the string to return to where it originally was. Extension springs are tightly wound metal wires structured like a coil, which is then normally fitted with hooks or loops at either end so that they attach easily to various components, equipment or fittings. These springs are used in the agricultural, automotive, consumer goods, electronics, energy and other industries.
Heavy-duty extension springs are also known by various names that include:
- Coil extension springs
- Coil tension springs
- Expansion springs
- Extension coil springs
- Helical extension springs
- High-tension springs
- Tension coil springs
- Tension springs
The extension springs used for heavy duty purposes normally are made from thicker steel wiring, with wider diameters overall. Heavy-duty extension springs can handle considerably greater forces than extension springs with smaller gauges.
Various Designs for Heavy-Duty Extension Springs
Heavy-duty extension springs feature an array of different end types and spring hooks, though there are several that are more commonly used.
These include:
- Closed German loop: Tightly wound into a small roundish loop at its end, these are designed to provide greater durability and strength for intensive applications in which springs must endure considerable force without distorting or releasing the loop.
- Double German loop: Featuring two loops at the spring’s endpoint, this design more securely attaches to components than other types of heavy-duty extension springs, keeping the spring from detaching when carrying a heavy load.
- English loop: Featuring a basic style of loop for the spring’s end, these extension springs generally have offset loops that aren’t centered but which are rather positioned to one side, which makes it easier to attach for applications where components aren’t in directly line with the spring’s axis.
- Extended German side loop: Similar to conventional German side loop designs, these differ due to the end loop’s greater length, which augments flexibility at the points where the spring attaches; these designs work well with specific angles or when heavy-duty springs need to connect over considerable distances.
- Extended side hook: With a raised hook on the side, this design offers greater flexibility in positioning; extension springs of this type tend to be used when they must attach to the component at some distance away.
- German side loop: Extending sideways from the spring’s end, these springs connect more easily, making them a good choice for applications in which they must attach at specific angles.
- Half German hook: This design features an open-ended loop for greater accessibility, allowing components to be quickly detached and reattached.
- Round-end hook: These commonly used extension springs feature a simple rounded loop at the end of the spring’s coil, providing a durable yet uncomplicated place at which the spring connects to other components.
- V hook: With an end shaped like a “V” to provide an unyielding but stable connection point, they work well for applications where heavy-duty extension springs must resist movement while also being precisely positioned.
There are other end types for heavy-duty extension springs as well, such as crew shackles and screw plugs. These types use specialized ends for applications that require a secure mechanical connection or need to operate in a more continuous manner. Crew shackles, for example, provide a sturdy and tough connection point for heavy loads, whereas screw plugs simply enable secure fastening of the spring in place.
Applications for Heavy-Duty Extension Springs
Various industrial sectors make use of these extension springs for multiple applications. This includes the agriculture, construction, fishing, mining and renewable energy sectors as well as motorsports.
Agriculture
Agricultural machinery like harvesters, ploughs, seeders and sprayers use these extension springs to close and open doors, gates and hatches through which interior components are accessed. They’re also used for managing internal components within these machines. Able to endure harsh outdoor conditions and weather, these springs can also withstand significant physical stress in often unforgiving environments.
Construction
Bulldozers, cranes, excavators and other construction equipment often make use of heavy-duty extension springs. They’re used to absorb jolts from components while in motion, balance hefty connectors and cope with strain in the control cabling of heavy machinery used in construction. The stress from continuous use on construction sites often makes construction equipment vibrate if not for these springs.
Fishing
Nets and traps used in the fishing sector often use these extension springs to operate. Ensuring that they close properly, springs built for commercial fishing applications need to tolerate wet conditions and the corrosion caused by saltwater.
Mining
For mines and quarries, heavy-duty extension springs are found in conveyors, crushers, drill rigs, pulverizers, vibrating screens and other mining equipment. Not only do they manage tension, but these springs also keep components like belts properly aligned. Additionally, they can absorb shock and vibrations during mining operations, while also protecting equipment from abrasive and weighty materials in difficult conditions.
Motorsports
All sorts of vehicles used in racing and other motorsports use these extension springs to deal with the extreme forces prevalent in such competitions. Braking systems use them to perform reliably while under significant stress, while suspension systems with these springs installed allow vehicles to better control rebounds from shocks. Additionally, these robust extension springs offer a means to precisely control return mechanisms. They enable vehicles to perform better, turn more sharply and even withstand recurrent collisions while also facilitating rapid acceleration.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy producing systems like solar trackers and wind turbines utilize systems containing heavy-duty extension springs. In solar arrays, they help solar panels track the sun to optimize the energy these systems produce. When used in wind turbines, they support their stability regardless of the wind conditions, helping to maintain tension in the control systems and cabling that adjust the pitch of the blades. These springs are often made from materials that resist corrosion, fluctuating temperatures and moisture.
Heavy-Duty Extension Springs from James Spring & Wire
James Spring & Wire Company carries a range of lighter gauge to heavy-duty extension springs with various end configurations. We can also customize extension springs for specific applications and industries with our experienced inhouse design and engineering team. To learn more about our capabilities or to request a quote, contact us directly.